end tidal co2 range dog
Thus ETCO 2 provides continuous noninvasive quantitation of adequacy of ventilation. Values above 40 - 45 mm Hg for ETCO.

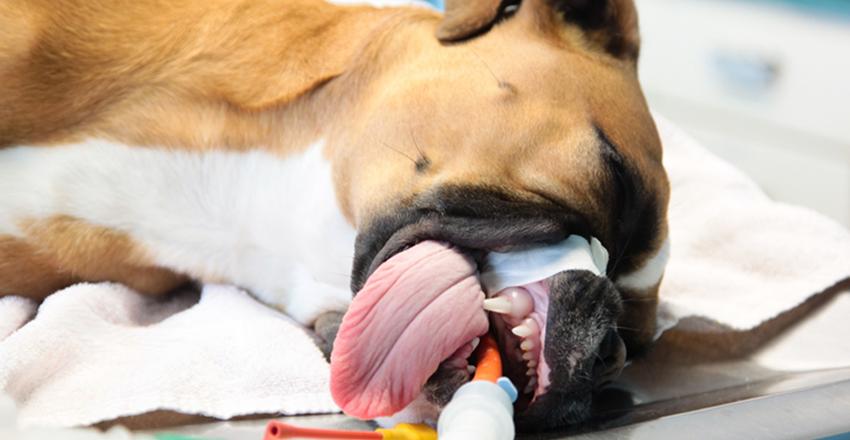
Concurrent Use Of Pulse Oximetry Via A Tongue Probe And Capnometry In An Anesthetized Dog Hemoglobin Saturatio Vet Medicine Vet Tech School Vet Tech Student
Variants of normal ETCO2 tracings from normal anesthetized animals.

. In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. Common narrow plateaus seen during. There was an excellent linear correlation b.
Assess the patients pulse and monitor end-tidal carbon dioxide production. Left untreated a state of hypercapnia can lead to death. Had end-tidal CO2 values in the range of those reported for healthy awake nonpanting adult beagle dogs 17.
Normal arterial blood pressure values for dogs and cats are indicated in Table 111. More Than Just a Number. Most anesthetics are respiratory depressants and end-tidal CO2 allows early detection of respiratory impairment so appropriate intervention can occur before the problem becomes life threatening.
Capnography can be used to measure end-tidal CO 2. Total pressure of a gas is the sum of the partial pressures of the gas Expired CO2 measured PetCO2 mmHg in waveform Percentage Normal Levels PaO2 85-100mmHg PaCO2 35-45mmHg Percentage vs. The end-tidal carbon dioxide will not necessarily reflect arterial carbon dioxide levels and the gradient between arterial and end-tidal carbon dioxide cannot.
78 Nitrogen 21 Oxygen 1 CO2 and other gases Exhaled gases. The normal end-tidal capnography wave form is basically a rounded rectangle. However an excess of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream can lead to an abnormal condition causing symptoms ranging from dizziness to convulsions.
It is also clear from Table I that the end-tidal CO2 response to 1 CO2 inhalation shows a small hypercapnia. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.
11172009 4 Measuring End Tidal CO2 Daltons Law. MmHg Relate to the air we breath. Since problems with lungs are not common and gas exchange between alveoli and the blood is swift and effective.
However because they are consistent over a wide range of pressures they are considered reliable Durham 2005. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. The end-tidal carbon dioxide tension PetCO2 measured after a single large tidal-volume breath 15 mlkg body weight was compared to simultaneous measurements of PaCO2 in 6 dogs with normal lungs who were receiving high-frequency jet ventilation HFJV.
The normal amount of carbon dixide in the arterial blood is 35-45 mm Hg a measurable unit of pressure. End-tidal CO2 monitoring is a non-invasive way to monitor a patients carbon dioxide levels. This is end-tidal CO 2 ETCO 2 which is normally 35 to 45 mm Hg in dogs and 28 to 32 mm.
Under most circumstances healthy pet no chest surgery end-tidal CO 2 is typically 5 10 mmHg less than arterial CO 2. Capnography waveforms etCO2 and breathing patterns. Examples of some common capnograms are.
For statistical comparisons of the responses the paired. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more. On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing.
Carbon dioxide is a normal part of. Available evidence has established that ETCO2 measurement can provide an indication of cardiac output and pulmonary blood flow24 Non. 11172009 4 Measuring End Tidal CO2 Daltons Law.
Love and Harvey 2006. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 is the level of carbon dioxide that is released at the end of an exhaled breath. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition.
ETCO2 levels reflect the adequacy with which carbon dioxide CO2 is carried in the blood back to the lungs and exhaled. Repiratory rate AND depth tidal volume which determine minute ventilation and therefore arterial CO2. In conditions of normal breathing 6 Lmin 12 breathsmin 500 ml for tidal volume etCO 2 is very close to alveolar CO2.
With a normal range of 35 - 45 mm Hg.

Anesthetic Monitoring Devices To Use And What The Results Mean Today S Veterinary Practice
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog

Anesthesia Machine Vet Medicine Vet Tech School Vet Technician

Veterinary Use Contec Ca10m Vet With 2 Gas Adapters Mainstream Etco2 C

Pdf Capnography In Dogs Semantic Scholar

Small Animal Anesthesia Techniques Ebook By Carolyn M Mckune Rakuten Kobo Small Pets Animals Veterinary Tech

Pdf Capnography In Dogs Semantic Scholar
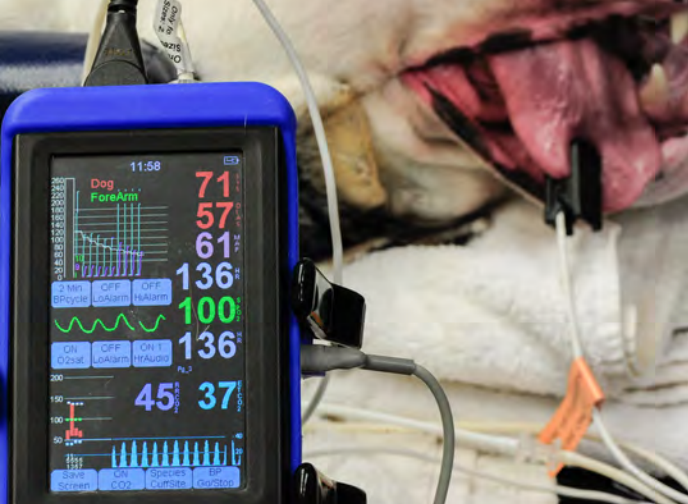
The Abcs Of Veterinary Dentistry V Is For Ventilation Monitoring

Veterinary Anesthesia Monitoring Cheat Sheet And Faqs

Pet Anesthesia And Patient Monitoring Westbridge Veterinary Hospital
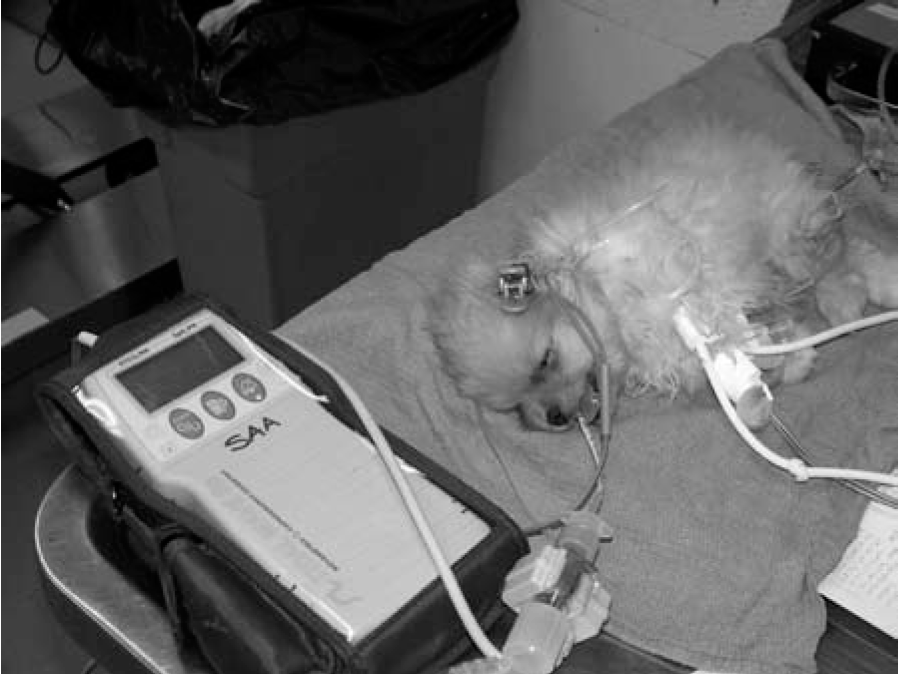
Capnography In Veterinary Medicine Chapter 28 Capnography
Did You Know Hypercapnia Is Synonymous With Hypoventilation

Etco2 Sensor Monitor Veterinary Cute Pet Capnography Monitor For Emergency Ac Dc Adapters Aliexpress

A Capnography Hack For Your Pint Sized Veterinary Patients

We Make 3d Selfie 3d Figurine Made Of Sandstone Just From Your Photo Pets Family Figurine Figurines

